Google's algorithm has undergone significant changes since its inception, with each update aimed at improving search results and user experience. In 2000, Google's algorithm was first introduced, using a simple ranking system that considered keyword density and link popularity.
Google's algorithm evolution has been shaped by several key updates, including the launch of PageRank in 2000, which revolutionized the way web pages were ranked. PageRank used a complex algorithm to analyze the importance of web pages based on the number and quality of links pointing to them.
In 2001, Google introduced the "Buffy" update, which aimed to reduce the effectiveness of link farms and low-quality websites. This update marked a significant shift towards a more sophisticated algorithm that could identify and penalize spammy websites.
Google's algorithm has continued to evolve, with the launch of Panda in 2011, which targeted low-quality content and thin websites.
You might enjoy: Pagerank Algorithm
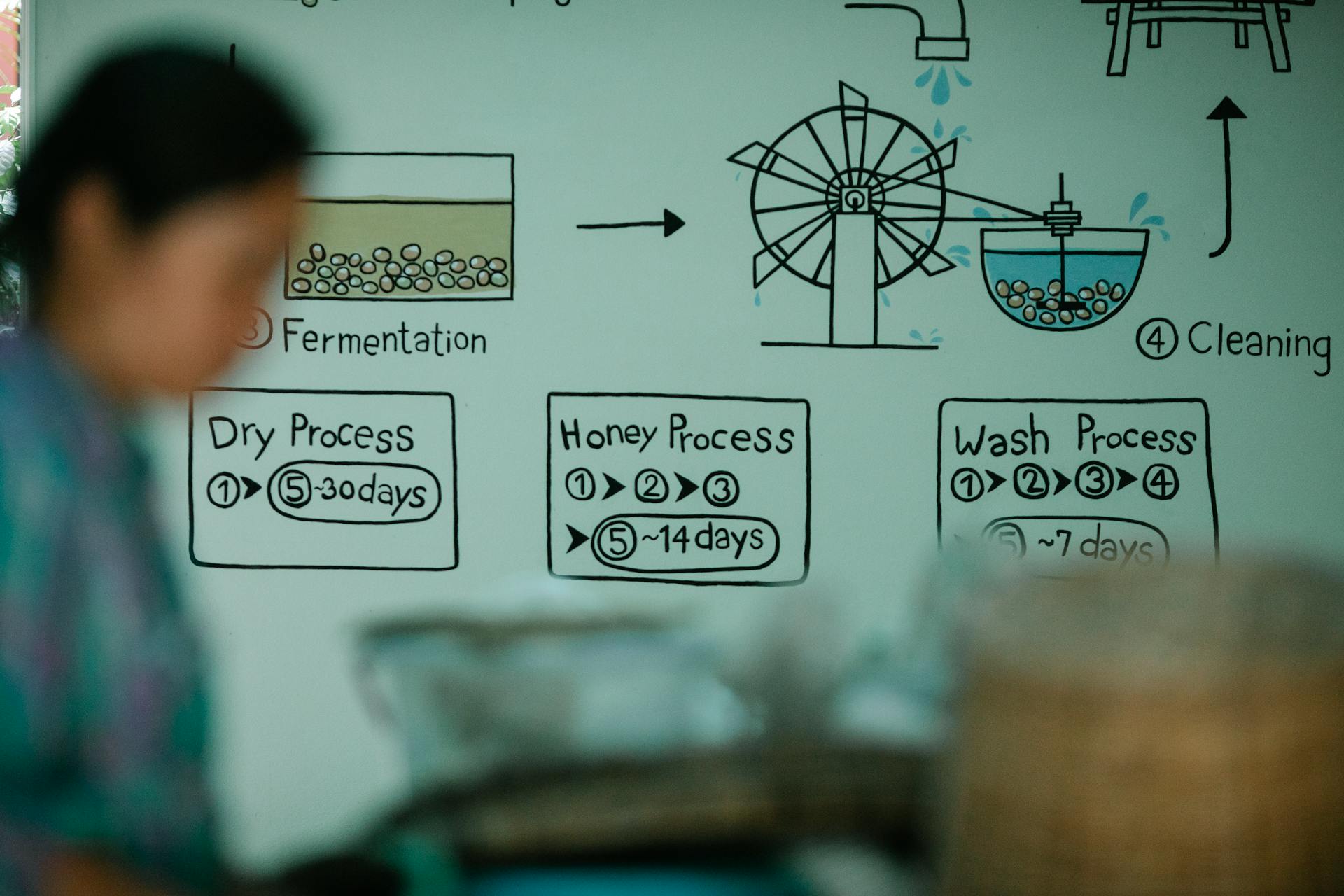
Google Algorithm History
Google's core algorithm has a history that dates back to the early 2000s, but a better understanding of Google today starts at 2010. During this time, Google made no releases to the public about its updates, leaving webmasters to speculate.
Google's core algorithm continues to evolve to serve its customers with quality content, with major updates expected in the next few years before Google solidifies its search engines.
People make over 4.7 billion Google searches every day, making it the most popular search engine among its competitors. This means the vast majority of your audience is actively searching Google for information your website or blog can deliver.
Curious to learn more? Check out: How Does the Google Search Algorithm Work
2003
In 2003, Google's search engine was already a powerhouse, with people making over 4.7 billion searches every day. This was a staggering number, and it's no wonder why Google was the go-to search engine for most users.
The exact number of ranking signals Google considers when displaying results isn't certain, but SEOs believe it includes factors like keyword usage, domain history, and site usability. These factors are crucial for optimizing on-page SEO, off-page SEO, and technical SEO.
As a result, businesses and marketers had to adapt to make their pages more discoverable by consumers actively searching Google for information. Google's algorithms were constantly evolving to improve the user experience and provide the most relevant results.
Google's algorithms determined the results you see for each search term, or query, by filtering through web content and reviewing indexed pages for relevance and quality. This process was crucial for ensuring that the right content was displayed to the right people.
A different take: Google Search Algorithm Documentation
The History of
Google's core algorithm has a long history, dating back to the early 2000s, but for a better understanding of Google today, it's more useful to start at 2010.
In 2010, Google made no releases to the public about its updates, so it was mainly Webmasters speculating about the changes.
Google Panda, which was assimilated into the core algorithm, is a permanent part of the search engine.
The core algorithm continues to evolve so Google can serve its customers with quality content.
Expect major updates in the next few years before Google solidifies its search engines.
Here's a brief timeline of some major updates:
- 2018: Google Medic Update, also known as the Core Algorithm Update, targeted quality issues like thin, duplicate content, slow load times, inaccurate title tags, and poor user experience.
- 2020: Featured Snippet Update, also known as Featured Snippet Deduplication, made it so that a website could only appear once per search page.
- 2021: Page Experience Update aimed to improve the user experience by giving priority to web pages with quick load times that stay stable as users scroll.
- 2022: Page Experience Update for Desktops built on top of the page experience update for mobiles, covering the Core Web Vitals metrics and their associated thresholds.
Note that this is not an exhaustive list, but it gives you a sense of the major updates that have shaped Google's algorithm over the years.
Featured Snippet Deduplication
Featured Snippet Deduplication was launched on January 22, 2020, with the goal of preventing URLs in featured snippets from appearing twice on the first page of organic search results.
This update aimed to make search results less cluttered and easier to navigate. The idea is that users can find an answer to their queries without having to sift through multiple listings from the same website.
The update was a response to the fact that websites could previously appear multiple times in the search results, including at the top as a featured snippet and again in the organic listings.
To illustrate this, consider a website that regularly updates its content, such as a blog with new posts each week. This type of website was a target of the Featured Snippets Update in August 2019, which aimed to surface snippets that would be better with frequent refreshes.
Here are some examples of types of websites that were targeted by the Featured Snippets Update in August 2019:
- Regularly updated information, like a blog with new posts each week
- Time-based information, like events or TV programming
- News and current events
These types of websites often have outdated snippets that can be removed and replaced with more relevant information.
Nothing
Google's algorithm history has been marked by significant updates aimed at improving search results. One notable example is the spam update.
Google constantly improves its AI algorithms to remove online scam from top results, detecting 40 billion spammy pages each day. This is a staggering number, and it's clear that Google takes online security seriously.
The algorithms have been successful in decreasing the amount of automatically generated or scraped content by 80% over several years. This is a remarkable achievement, and it shows the effectiveness of Google's efforts.
Google's algorithms detect and thwart various black-SEO techniques, including link schemes, keyword stuffing, sneaky redirects, doorway pages, cloaking, and thin content. These techniques are often used by spammers to manipulate search engine rankings.
Some of the specific black-SEO techniques targeted by Google include low-value, ad-centered content and thin, affiliate-heavy content. These types of content are often created solely for the purpose of generating revenue, rather than providing value to users.
Here are some examples of black-SEO techniques that Google's algorithms detect:
- Link schemes
- Keyword stuffing
- Sneaky redirects
- Doorway pages
- Cloaking
- Thin content
- Low-value, ad-centered content
- Thin, affiliate-heavy content
Notable Algorithm Updates
Google has made several notable algorithm updates over the years, aiming to improve search results for users.
One such update was the Google Updates 2014, which included various changes to enhance the search experience.
Google put out a Core Algorithm Update on March 9, 2018, to better judge which sites were relevant for specific queries. This update was designed to help improve rankings for sites with useful content.
2005
In 2005, Google introduced the Google AdWords algorithm update, which significantly improved the relevance of ads displayed on search results pages.
This update focused on keyword matching, allowing advertisers to target specific keywords and phrases, resulting in more precise ad placements.
The update also introduced Quality Score, a metric that evaluated ad relevance, landing page quality, and click-through rates to determine ad position and cost.
As a result, advertisers could now optimize their campaigns more effectively, leading to better ROI and increased ad visibility.
Google's algorithm update in 2005 marked a significant shift towards more targeted and relevant advertising, ultimately benefiting both advertisers and users.
2012
In 2012, Google rolled out the Exact Match Domain Update on September 28, which targeted websites with domains that exactly matched competitive keywords, often used to boost search placement despite poor quality or thin content.
Websites that relied on this practice saw their value plummet.
This update marked a shift in Google's focus towards quality content over keyword manipulation.
Hummingbird (2013)
In 2013, Google expanded its Knowledge Graph and started using semantic markup like schema.org to determine additional search results, such as in-depth articles.
Google released the Hummingbird Update on September 26, 2013, to provide a more conversational, human search experience. This update improved upon the Knowledge Graph feature.
Hummingbird uses natural language processing, including semantic indexing, synonyms, and other features, to interpret queries and produce results. It weeds out keyword-stuffed, low-quality content to create a more personalized, exact search process.
Spammy sites are those that use spam techniques like spamdexing or black hat SEO techniques. These sites try to manipulate search results for their own gain.
The Hummingbird Update was launched on August 22, 2013, and its goal is to produce more relevant search results by better understanding the meaning behind queries.
Additional reading: Hummingbird Algorithm Google
2014
2014 was a significant year for Google's algorithm updates. Google made a change to the way local results are displayed through its Pigeon update. This update integrated local results with the rest of the search results while not fully assimilating with the core algorithm.
Google also started giving preference to secure sites, preferring them over insecure versions and giving them a small bump in authority. This boost began small but increased over time as webmasters had the chance to react.
Another quality update was speculated to be released early in the year, but Google never made an official announcement.
If this caught your attention, see: Google Local Ranking
RankBrain (2015)
In 2015, Google released its mobile update, which penalized unoptimized websites in rankings and sometimes cut their search traffic in half. This update was a game-changer for mobile users, making it essential for websites to have a mobile-friendly design.
RankBrain was introduced on October 26, 2015, as part of the Hummingbird update. It's a machine-learning-powered component of Google's algorithm that helps understand searcher intent.
RankBrain measures how searchers interact with search results and ranks them accordingly. This means that the same search query can yield different results depending on your search history and behavior.
The RankBrain algorithm identifies relevance features for websites that rank for a given query, establishing query-specific ranking factors and signals. This helps Google deliver the most accurate and relevant search engine results pages (SERPs).
2017
In 2017, Google made a significant update to their algorithm targeting sites with low-quality content focused on revenue generation.
This update, known as "Fred", marked another step in Google's efforts to reward sites that provide valuable content, not just those trying to earn a quick buck.
The "Fred" update specifically impacted sites that were ad-heavy and lacked quality content, signaling a shift in Google's priorities.
Check this out: Google Fred Algorithm
2018
In 2018, Google put out a core algorithm update to better judge which sites were relevant for specific queries.
This update was to help improve rankings for sites with useful content.
Google's goal with this update was to make search results more accurate and helpful for users.
The update rolled out on March 9, 2018, and was a significant change to how Google evaluates websites.
2019
In 2019, Google's BERT algorithm update significantly impacted search engine results.
BERT improved the accuracy of search results by understanding the context and nuance of search queries.
The update led to a 10% increase in accurate search results for certain types of searches.
Google's algorithm update also made it easier for users to find what they're looking for by understanding the intent behind their search queries.
In 2019, Google's algorithm update also impacted the way websites were ranked in search engine results.
Websites that provided accurate and relevant information were more likely to rank higher in search engine results.
The update also made it more difficult for websites to manipulate their rankings through keyword stuffing and other tactics.
2020
In 2020, Google rolled out a broad core algorithm update on December 3, which was a massive update that caused SERPs volatility, although the impact was unclear.
Many SEOs noticed that some domains reported gains while others reported losses, making it hard to determine the effects of the update.
The update occurred right in the middle of the holiday shopping season, which raised questions about Google's timing.
Google's guidance on such updates remains the same, and it's still focused on E-A-T quality guidelines, which are essential for high-quality content.
The December 2020 update was just one of the many algorithm updates that Google releases throughout the year, and it's essential to stay up-to-date with these changes to maintain a strong online presence.
Google's product algorithm update in March 2022 made it easier to find high-quality reviews through search, which aligns with user feedback that people prefer detailed reviews with evidence of products being tested.
Reviews
Reviews are a crucial aspect of the Google algorithm updates, and several notable updates have been made to improve the quality and relevance of product reviews in search results.
In March 2022, Google announced a Product Algorithm Update that makes it easier to find high-quality reviews through search. This update was aimed at helping users find detailed reviews with evidence of products actually being tested.
Google has also introduced a new site-wide ranking signal based on machine learning as part of the Helpful Content Update in December 2022. This update targets content created with the sole purpose of ranking and downranks sites with a lot of unhelpful content.
The July 2022 Product Reviews Update was completed on August 2nd, and it's essential for ecommerce marketers to know how to write high-quality product reviews to improve their rankings. Google's documentation on how to write high-quality product reviews is a great resource for site owners.
Here's a brief summary of the notable product review updates:
These updates demonstrate Google's commitment to providing users with accurate and helpful information, and site owners should take note of these changes to improve their SEO strategies.
BERT and Featured Snippets
BERT was a significant search algorithm update launched on October 25, 2019, and rolled out on December 9, 2019. It aimed to help the search engine understand context, especially in spoken queries.
This update was a deep-learning technique created for natural language processing, and Google named BERT as “one of the biggest leaps in the last five years”. It was particularly needed since the spread of voice search assistants, and Google rolled out its first BERT update for the English language, and then for over 70 other languages.
The BERT update allowed Google to capture more of the nuance and context in queries and not lean so heavily on the use of prepositions or phrasing to clarify questions. It was applied to featured snippets in over two dozen countries and languages, helping users find useful and accurate information.
Featured snippets were also updated in August 2019 to surface snippets that would be better with frequent refreshes. This update targeted snippets with regularly updated information, time-based information, and news and current events.
BERT (2019)
BERT was launched on October 25, 2019, and it's a deep-learning technique created for natural language processing.
This technique inside the ranking algorithm was particularly needed since the spread of voice search assistants.
Google named BERT as “one of the biggest leaps in the last five years”.
The BERT update allows Google to capture more of the nuance and context in queries and not lean so heavily on the use of prepositions or phrasing to clarify questions.
BERT was applied to featured snippets in over two dozen countries and languages.
Google rolled out its first BERT update for the English language, and then for over 70 other languages.
Earlier reports said BERT had affected 10% of all search queries.
Featured Snippets (Aug 2019)
Featured Snippets (Aug 2019) were a major update aimed at improving the way Google surfaces snippets in search results. This update was launched on August 1, 2019, with the goal of making featured snippets better and more relevant to users.
The update specifically targeted three types of content: regularly updated information, time-based information, and news and current events. This makes sense, as these types of content are often the most dynamic and prone to change.
For more insights, see: Google Algorithm Update March 2019
Regularly updated information, like a blog with new posts each week, was a key focus of this update. Time-based information, such as events or TV programming, was also a target. And, of course, news and current events were also a priority.
This update helped to remove outdated snippets and surface new, more relevant ones. The goal was to make search results more accurate and helpful for users.
Frequently Asked Questions
What was the first Google algorithm?
The first Google algorithm was PageRank, developed by Larry Page and Sergey Brin in 1998. PageRank estimated a website's importance by counting the number and quality of links to it.
What was Google's original algorithm?
Google's original algorithm was PageRank, a pioneering ranking system that laid the foundation for the company's search results. This algorithm remains the most well-known, although it's no longer the sole ranking method used by Google.
Sources
Featured Images: pexels.com